Physical and Chemical Properties of Aluminum and aluminum alloys
1412 Views 2024-04-17 09:31:35
Physical and Chemical Properties of Aluminum and aluminum alloys
Although aluminum and aluminum alloys both use aluminum as the main synthetic element, they have great differences in certain physical and chemical properties.
Aluminum is a lightweight and very active element that is easily oxidized with oxygen in the air. Aluminum and aluminum alloys often use these two characteristics, which are also the most outstanding physical and chemical properties of aluminum.

Physical and Chemical Properties of Aluminum and aluminum alloys
Physical properties of aluminum
Aluminum itself is a very soft object, but after being synthesized with other elements, the hardness of aluminum alloy is much higher than that of aluminum, and can even be comparable to steel.
| Property | Description |
| Symbol | Al |
| Atomic Number | 13 |
| Atomic Mass | 26.9815 g/mol |
| Phase at Room Temp. | Solid |
| Density | 2.70 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 660.32°C (1220.58°F) |
| Boiling Point | 2467°C (4472.6°F) |
| Color | Silvery-White |
| Malleability | Highly Malleable |
| Ductility | Highly Ductile |
| Conductivity | Thermal and Electrical Conductor |
| Tensile Strength | Relatively Low (Can be Strengthened) |
| Hardness | Relatively Soft (Pure Aluminum) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Forms Protective Oxide Layer) |
| Crystal Structure | Face-Centered Cubic (FCC) |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-Magnetic |
| Thermal Expansion | 23.1 x 10^-6 /°C (at 25°C) |
| Young’s Modulus | 68.3 GPa (9860 ksi) |
| Shear Modulus | 26 GPa (3770 ksi) |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.33 |
| Specific Heat Capacity | 0.897 J/g°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 237 W/(m·K) at 25°C |
| Electrical Conductivity | 37.7 x 10^6 S/m (IACS) |
| Resistivity | 2.65 x 10^-8 ohm-m |
| Reflectivity | Approximately 80% for visible light |
Chemical Properties of Aluminum
Aluminum is very active in nature, making it difficult to purify aluminum. Aluminum can easily react with oxygen in the air to form harder aluminum oxide. People often use this property to improve the hardness of aluminum alloy surfaces.
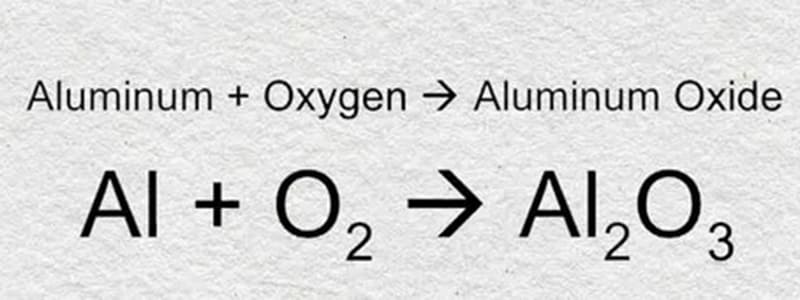
Oxidation of Aluminum
| Property | Description |
| Reactivity with Oxygen | Reacts with oxygen to form aluminum oxide (Al2O3), which provides a protective layer against further oxidation. This layer is stable and prevents the metal from corroding. |
| Reactivity with Acids | Reacts with acids such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) or sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to produce aluminum salts and hydrogen gas. The reaction is more vigorous with concentrated or hot acids. |
| Reactivity with Bases | Reacts with strong bases like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce aluminum salts and hydrogen gas. The reaction is also quite vigorous. |
| Reactivity with Halogens | Reacts with halogens (e.g., chlorine, bromine) to form aluminum halides (e.g., AlCl3, AlBr3). These reactions are typically vigorous and can occur at room temperature. |
| Combustibility | While not flammable in the traditional sense, aluminum can burn in powder, flakes, or thin strips, producing aluminum oxide and heat. This is known as a thermite reaction and is used in welding and pyrotechnics. |
| Passivation | Aluminum is capable of passivation, forming a thin, protective oxide layer on its surface that prevents further oxidation. This property contributes to its excellent corrosion resistance. |
| Reaction with Water | Aluminum does not react with water at room temperature due to the presence of the oxide layer. However, at high temperatures, it can react with steam to produce aluminum oxide and hydrogen gas. |
| Alloy Formation | Aluminum readily forms alloys with other metals, altering its chemical properties and enhancing its mechanical and physical properties for specific applications. Common alloying elements include copper, silicon, and magnesium. |
Applications of different series of aluminum alloys
The properties of aluminum alloys vary greatly due to different synthetic elements. According to the main synthetic elements of aluminum alloys, aluminum alloys can be divided into 1000-8000 series aluminum alloys.
| Aluminum alloy series | Main alloying elements | Application |
| 1000 Series | Almost pure Aluminum | Food processing equipment, chemical processing equipment, etc. |
| 2000 Series | Cu | Structural components in the aerospace and aviation industry |
| 3000 Series | Mn | Fuel tank, cylinder wall and other components |
| 5000 Series | Mn & Mg | Ship, automotive and aircraft parts |
| 6000 Series | Si & Mg | Structural components in the construction, aerospace and automotive industries |
| 7000 Series | Zn | High-strength components in aerospace and sports equipment |
| 8000 Series | Fe | Packaging materials such as aluminum foil |