1. Introduction
ISO certified aluminum foil represents a high standard of consistency, safety, and quality assurance across a wide range of industrial and consumer applications.
While aluminum foil is a widely utilised material—from food wrapping and household preservation to blister packaging, automotive insulation, and electromagnetic shielding—its performance is determined by alloy composition, surface cleanliness, thermal resistance, pinhole level, thickness tolerance, and mechanical reliability.
ISO certification provides verifiable proof that manufacturers consistently meet internationally accepted management, environmental, and safety standards.
More importantly, ISO compliance gives users confidence that aluminium foil is safe for food, medicine, and sensitive performance-critical products.

ISO Certified Aluminum Foil
2. Understanding ISO Certification: Foundations and Relevance
What is ISO and Its Global Mandate
ISO—the International Organisation for Standardisation—was established in 1947 and today includes more than 167 member countries.
ISO does not manufacture products or issue regulatory laws; instead, it develops globally recognised standards related to manufacturing processes, risk management, resource control, environmental sustainability, and product testing.
ISO certification is performed by accredited third-party agencies that audit companies based on:
- documented process control
- continuous improvement
- product traceability
- safety compliance
- regulatory alignment
Companies that meet ISO standards receive certificates valid for typically three years, with annual surveillance audits.
In the case of aluminum foil manufacturing, ISO reinforces:
- consistent alloy composition
- controlled rolling parameters
- defined tolerance limits
- hygienic processing and packaging
This translates into fewer defects, improved product performance, and reduced customer complaints.
Key ISO Standards Relevant to Aluminum Foil
While ISO publishes over 24,000 standards, only a few directly influence aluminum foil production and usage. Among them:
| ISO Standard | Core Focus | Relevance to Aluminum Foil |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality control system | Gauge consistency, defect control, batch traceability |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental management | Waste, emissions, and recycling control |
| ISO 22000 / FSSC 22000 | Food safety management | Migration safety, contamination prevention |
| ISO 15378 | Pharma packaging compliance | Primary pharmaceutical packaging and GMP |
| ISO 45001 | Occupational health/safety | Mill safety, hazardous operations |
| ISO 50001 | Energy management | Heat/rolling energy efficiency |
These frameworks unify technical, compliance, and operational requirements across global markets.
ISO Certification vs. Other Certifications
| Certification Type | Description | Impact on Aluminum Foil |
|---|---|---|
| ISO Certification | Comprehensive system certification | Ensures management, traceability, and stable processes |
| FDA Compliance | U.S. food contact approval | Approves the food safety composition |
| EU 1935/2004 | EU contact materials regulation | Governs safe materials entering food |
| RoHS/REACH | Hazardous substances control | Focused on chemical compliance |
| TÜV Certification | Third-party quality and performance testing | Product safety validation |
Key distinction:
ISO certifies the management system responsible for quality, not the product itself. Buyers benefit when ISO certification is paired with product-specific compliance tests.

Huawei Packaged Aluminum Foil
3. Why ISO Certification Matters for Aluminum Foil
ISO certification ensures that aluminum foil meets performance expectations consistently. Typical performance values include:
| Performance Indicator | Typical Value for ISO-Compliant Foil |
|---|---|
| Thickness tolerance | ±3% to ±6% depending on grade |
| Tensile strength (8011-H18) | ≥ 120 MPa |
| Pinhole density | ≤ 3 per m² for pharma foil |
| WVTR (with coating/lamination) | < 1 g/m²·day |
| OTR (oxygen barrier) | < 0.1 cm³/m²·day |
ISO certification matters because it ensures:
✓ Safety
No harmful residues, lubricants, or contaminants enter food or medicine.
✓ Quality reproducibility
Reduced variation in thickness or alloy performance.
✓ Traceability
Every roll can be traced to raw material batches.
✓ Risk reduction
Lower probability of recall or product failure.
✓ Market recognition
ISO compliance is often mandatory for export contracts.

HVAC Used ISO Certified Aluminum Foil
4. Common Alloys of ISO Certified Aluminum Foil
ISO certification does not define alloy types directly; however, certain alloys dominate aluminum foil manufacturing due to their mechanical behavior, forming characteristics, corrosion resistance, and food-/medicine-safe composition.
ISO-certified production ensures that their properties—such as chemical composition, tensile strength, elongation and pinhole resistance—remain consistent from batch to batch with full traceability.
| Alloy | Typical Temper | Mechanical Properties (Typical Range) | Key Attributes | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1100 | O, H14, H18 | Tensile: 60–100 MPa Elongation: 20–40% | Excellent ductility, high formability, high corrosion resistance | Household foil, flexible packaging, insulation foils, nutrition wrap |
| 1145 | O, H19 | Tensile: 65–110 MPa Elongation: 16–35% | High purity (>99% Al), low migration risk, excellent barrier properties | Cigarette foil, food sealing foil, aseptic packaging |
| 1235 | O, H18 | Tensile: 70–120 MPa Elongation: 12–28% | Superior ductility, high workability, low pinhole susceptibility | Household foil, converter foil, lamination-grade foil |
| 3003 | O, H24 | Tensile: 90–130 MPa Elongation: 10–25% | Better mechanical strength vs. pure aluminum, improved crack resistance | Aluminum containers, food trays, semi-rigid packaging |
| 8011 | O, H18, H22 | Tensile: 100–150 MPa Elongation: 8–25% | Widely used for packaging; high barrier performance; good sealing | Medicine packaging, household heavy-duty foil, food container lids |
| 8021 | O | Tensile: 90–140 MPa Elongation: 10–30% | High tensile stability and enhanced pinhole resistance | Pharmaceutical cold-form foil, deep-draw foil, laminated barrier foil |
| 8079 | O | Tensile: 90–120 MPa Elongation: 10–25% | High elongation and low thickness variation | Converter foil, composite laminates, high-barrier food packaging |
5. Relevant ISO Standards (overview and relevance)
Below are the principal ISO standards that matter for aluminum foil production and supply. Each has a distinct focus and practical consequences.
ISO 9001 — Quality Management System (QMS)
Scope: Process control, document management, calibration, supplier control and continuous improvement.
Relevance: Ensures mills have documented sampling plans, calibrated thickness gauges, defined acceptance criteria and CAPA procedures.
What buyers can expect: routine MTR/COA issuance, documented non-conformance handling, and records retention for audits.
ISO 14001 — Environmental Management System (EMS)
Scope: Environmental impacts, waste handling, emissions, resource use and continual environmental improvement.
Relevance: Important where buyers require low VOC coatings, responsible scrappage management and demonstrable recycling programs.
What buyers can expect: documented waste streams, recycling rates for trim scrap and evidence of emissions control.
ISO 22000 / FSSC 22000 — Food Safety Management
Scope: HACCP-based food safety control systems covering hazard analysis, CCPs, hygiene, contamination control and traceability.
Relevance: Required or preferred for aluminum foil that directly contacts food (retort foil, blister lidding, cook-in-bag).
What buyers can expect: CCP monitoring records (e.g., pinhole checks, lubricant removal), hygienic packaging processes and supplier control for inks/adhesives.
ISO 15378 — Primary Packaging Materials for Medicinal Products
Scope: GMP-aligned requirements specifically for primary packaging used in medicines (e.g., blister foil).
Relevance: For pharmaceutical buyers, ISO 15378 supplies the audit trail and process controls regulators expect.
What buyers can expect: full batch traceability, validated cleaning/sterilization where applicable, extended retention of records.
ISO 45001 — Occupational Health & Safety
Scope: Worker safety systems and risk control.
Relevance: Rolling mills involve heavy loads, high temperatures and sharp edges; ISO 45001 reduces accident risk and business disruption.
What buyers can expect: evidence of safety programs, training records and incident investigation procedures.
ISO 50001 — Energy Management (optional relevance)
Scope: Systematic energy performance improvement.
Relevance: For energy-intensive rolling operations, ISO 50001 demonstrates efficiency and can be used in sustainability claims.
What buyers can expect: energy KPIs, initiatives for waste-heat recovery and improved carbon accounting.

8021 ISO Certified Aluminum Foil for Food Packaging
6. How ISO Certification Intersects with Product & Process Requirements for Foil
ISO systems provide the framework; product performance depends on controlled execution and supporting tests.
This section ties ISO requirements to the metrics that matter to foil users.
Material quality and traceability
ISO systems require documented incoming inspection and supplier appraisal. Practically that means for aluminum foil:
- Raw material MTRs (ingot/cast billet chemistry) are retained and linked to finished coil IDs.
- Lot traceability: each finished roll has a unique identifier tied to process records (rolling schedule, anneal, slitting).
This allows rapid root-cause analysis if a downstream defect appears.
Process control (rolling, annealing, slitting)
Key variables to control and document:
- Rolling pass reduction and cumulative thickness reduction schedules (affect microstructure and strength).
- Anneal temperature and hold time (affect temper, elongation and forming characteristics).
- Slitting tension and edge control (affect edge quality and telescoping risk).
ISO requires procedures, monitoring records, and deviation handling.
Quality control and test methods (thickness, tensile, puncture, pinholes)
ISO 9001 mandates documented test methods and calibrated equipment. Typical QC program elements:
- Thickness: continuous in-line eddy-current gauging plus off-line micrometer checks.
- Gravimetric check: mass per area → thickness calculation using density ρ = 2.70 g/cm³:mass (g/m²)=2.70×thickness (µm).\text{mass (g/m²)} = 2.70 \times \text{thickness (µm)}.mass (g/m²)=2.70×thickness (µm).Example: 24 µm → mass = 2.70 × 24 = 64.8 g/m².
- Tensile testing: per ASTM/EN methods to verify tensile strength and elongation.
- Pinhole inspection: visual/optical plus electronic conductivity tests; specify allowable pinholes per m².
- Puncture resistance: bench tests with defined indenter geometry and energy/force threshold.
ISO systems specify calibration frequency (e.g., micrometers every 3–6 months, tensile frames annually) and document calibration certificates.
Supplier management and incoming material control
ISO requires supplier audits, certificate review and re-qualification metrics. For foil:
- verify secondary aluminum content (recycled material) and impurity limits;
- verify coatings/inks adhesives have appropriate food/pharma approvals.
Documentation & traceability (MTR, COA, batch IDs)
ISO requires retention of MTRs and COAs and linkage to finished product IDs.
For pharma or food, this documentation is often required by the downstream converter for their regulatory files.
7. Application Scenarios of ISO-Certified Aluminum Foil
Below are practical application scenarios showing how ISO certification enhances value.
Food Packaging
Examples: retort pouches, ovenable trays, confectionery wrap, ready-meal laminates.
Why ISO helps: ISO 22000 / FSSC 22000 plus ISO 9001 ensure contaminant control, validated cleaning of slitting lines, and traceable batch records.
Important product metrics: thickness tolerance (e.g., 24 µm ±4%), pinhole number ≤ 2/m² (food-grade), migration test compliance per FDA/EU limits.
Pharmaceutical Packaging
Examples: cold-form blister foil, level-of-protection blister lidding.
Why ISO helps: ISO 15378 (or equivalent GMP) is often a contractual requirement. Buyers expect ≤1 pinhole/m², thickness tolerance ±3%, and full batch-to-drug-batch traceability.
Industrial & Automotive
Examples: HVAC insulation facers, heat shields, EMI shielding layers, battery foil backing.
Why ISO helps: ISO 9001 ensures consistent gauge and surface properties; ISO 14001 and ISO 50001 support sustainability claims.
Important metrics: reflectivity (>85% for certain insulation foils), mechanical strength for forming operations (tensile 100–150 MPa depending on alloy).
Sustainable Applications
Examples: circular packaging, post-consumer recycling pathways, energy-efficient foil rolling.
Why ISO helps: ISO 14001 and ISO 50001 demonstrate environmental management, energy efficiency and documented scrap recycling rates — useful for corporate ESG reporting and for buyers seeking low-carbon supply chains.
8. Conclusion
ISO certified aluminum foil represents a significant advance in verifying metal quality, manufacturing consistency, and global compliance.
Standards such as ISO 9001, ISO 15378, and ISO 22000 ensure traceability, documented test methods, and contamination control.
ISO certification not only enhances consumer safety but also improves line performance, reduces scrap rates, and supports sustainable industrial development.
For buyers, ISO compliance means fewer quality disputes, assured regulatory acceptance, and stable long-term supply.
FAQs
Q1 — Does ISO 9001 certify the foil itself?
No. ISO 9001 certifies the manufacturer’s quality management system, not the product. Buyers should require product testing (MTR/COA) in addition to ISO certificate.
Q2 — Which ISO standard is essential for food-contact foil?
ISO 22000 (or FSSC 22000) addresses food safety systems; for food contact materials this should be paired with migration testing to relevant legal limits (EU/FDA).
Q3 — How tight should thickness tolerances be?
Typical tolerances: ±3% for high-precision pharma foil; ±4–6% for heavy-duty or standard household foil — always specify in the purchase order.
Q4 — How often are ISO certificates audited?
After initial certification, registrars usually perform annual surveillance audits and a full recertification audit every three years.
Q5 — What is a defensible pinhole limit?
For pharmaceutical primary packaging ≤1 pinhole/m² is common; for food packaging 1–5 pinholes/m² may be acceptable depending on application and barrier requirements. Always define the method used to detect pinholes.
Casting production process and its introduction
The purpose of melting and casting is to produce alloys with satisfactory composition and high purity of melt, so as to create favorable conditions for casting alloys of various shapes.
Melting and casting process steps: batching --- feeding --- melting --- stirring after melting, slag removal --- pre-analysis sampling --- adding alloy to adjust the composition, stirring --- refining --- static Setting——Guide furnace casting.
Hot rolling production process and its introduction
- 1. Hot rolling generally refers to rolling above the metal recrystallization temperature;
- 2. During the hot rolling process, the metal has both hardening and softening processes. Due to the influence of deformation speed, as long as the recovery and recrystallization process is too late, there will be a certain work hardening;
- 3. The recrystallization of the metal after hot rolling is incomplete, that is, the coexistence of recrystallized structure and deformed structure;
- 4. Hot rolling can improve the processing performance of metals and alloys, reduce or eliminate casting defects.
- 1. The casting and rolling temperature is generally between 680°C and 700°C. The lower the better, the stable casting and rolling line usually stops once a month or more to re-stand. During the production process, it is necessary to strictly control the liquid level of the front tank to prevent low liquid level;
- 2. Lubrication uses C powder with incomplete combustion of gas for lubrication, which is also one of the reasons for the dirty surface of casting and rolling materials;
- 3. The production speed is generally between 1.5m/min-2.5m/min;
- 4. The surface quality of products produced by casting and rolling is generally relatively low, and generally cannot meet products with special physical and chemical performance requirements.
- 1. Cold rolling refers to the rolling production method below the recrystallization temperature;
- 2. There will be no dynamic recrystallization during the rolling process, and the temperature will rise to the recovery temperature at most, and the cold rolling will appear in a work hardening state, and the work hardening rate will be large;
- 3. The cold-rolled sheet and strip have high dimensional accuracy, good surface quality, uniform structure and performance, and products in various states can be obtained with heat treatment;
- 4. Cold rolling can roll out thin strips, but at the same time, it has the disadvantages of high energy consumption for deformation and many processing passes.
- 1. Finishing is a processing method to make the cold-rolled sheet meet the customer's requirements, or to facilitate the subsequent processing of the product;
- 2. The finishing equipment can correct the defects produced in the hot rolling and cold rolling production process, such as cracked edge, oily, poor plate shape, residual stress, etc. It needs to ensure that no other defects are brought into the production process;
- 3. There are various finishing equipments, mainly including cross-cutting, slitting, stretching and straightening, annealing furnace, slitter, etc.
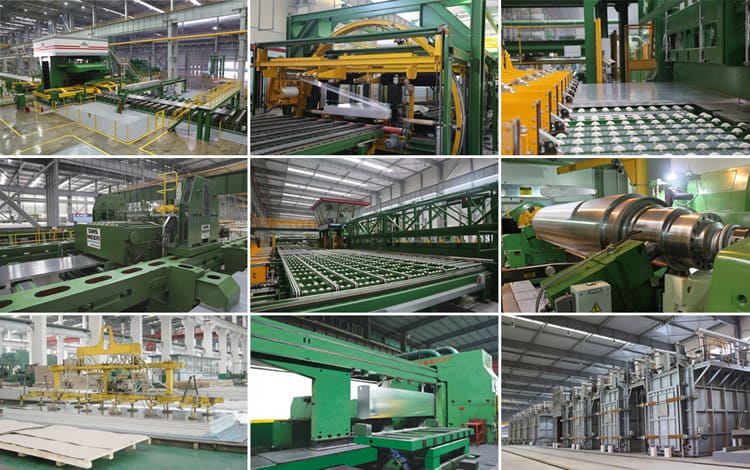

Casting and rolling process
Casting and rolling process: liquid metal, front box (liquid level control), casting and rolling machine (lubrication system, cooling water), shearing machine, coiling machine.
Cold rolling production process

Introduction to finishing production process
Aluminum alloy has the characteristics of low density, good mechanical properties, good processing performance, non-toxic, easy to recycle, excellent electrical conductivity, heat transfer and corrosion resistance, so it has a wide range of applications.
Aerospace: used to make aircraft skins, fuselage frames, girders, rotors, propellers, fuel tanks, wall panels and landing gear struts, as well as rocket forging rings, spacecraft wall panels, etc.
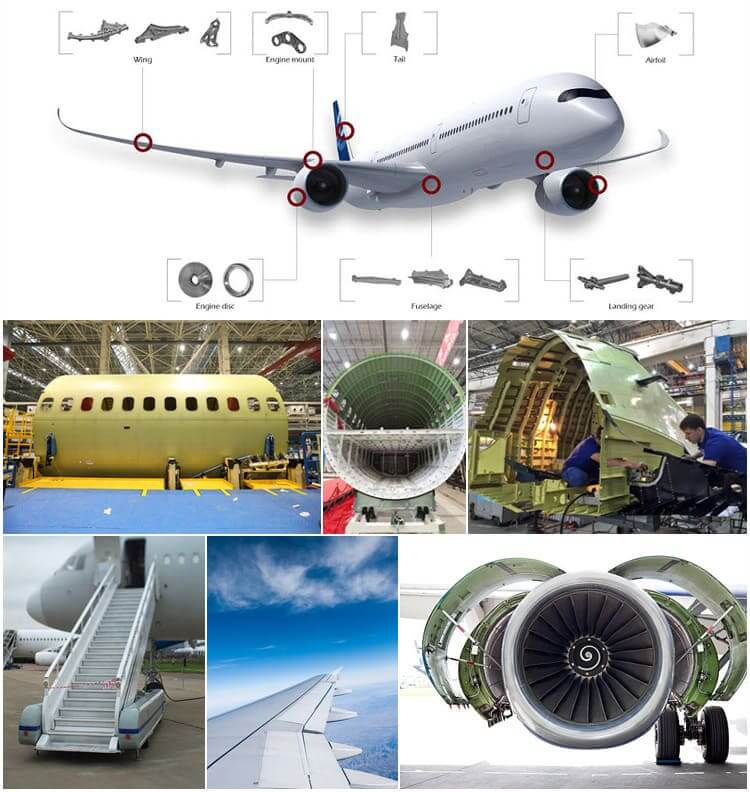

Aluminum alloy used for aerospace
Transportation: used for car body structure materials of automobiles, subway vehicles, railway passenger cars, high-speed passenger cars, doors and windows, shelves, automotive engine parts, air conditioners, radiators, body panels, wheels and ship materials.
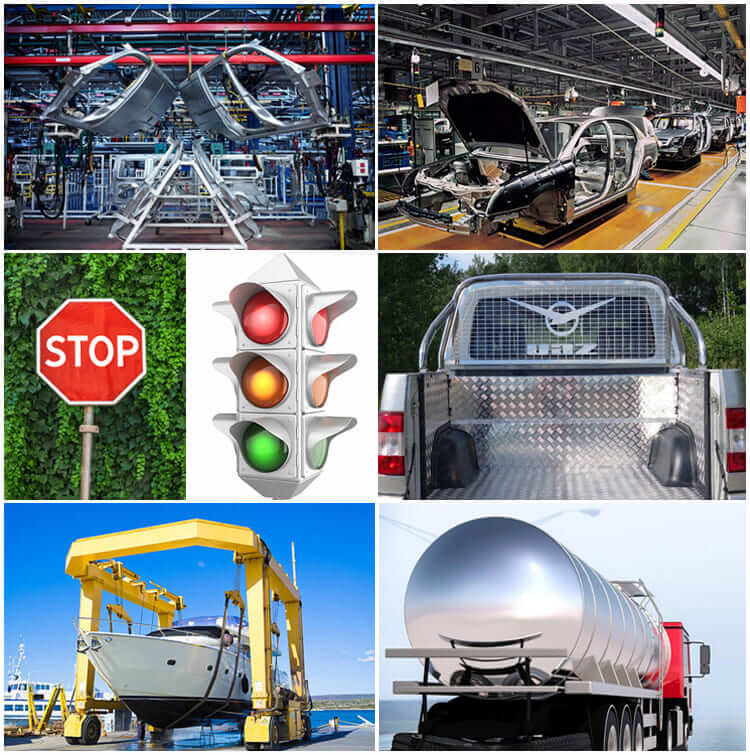

Traffic application
Packaging: All-aluminum pop cans are mainly used as metal packaging materials in the form of thin plates and foils, and are made into cans, lids, bottles, barrels, and packaging foils. Widely used in the packaging of beverages, food, cosmetics, medicines, cigarettes, industrial products, medicines, etc.
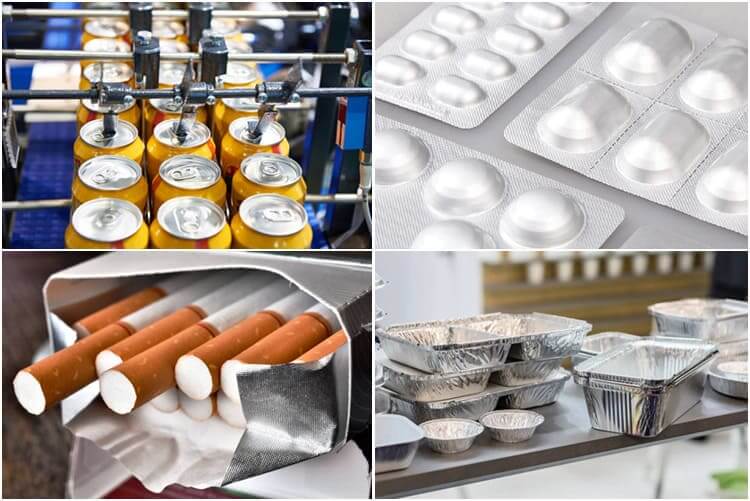

Packaging application
Printing: Mainly used to make PS plates, aluminum-based PS plates are a new type of material in the printing industry, used for automatic plate making and printing.
PS printing
Architectural decoration: aluminum alloy is widely used in building structures, doors and windows, suspended ceilings, decorative surfaces, etc. due to its good corrosion resistance, sufficient strength, excellent process performance and welding performance.
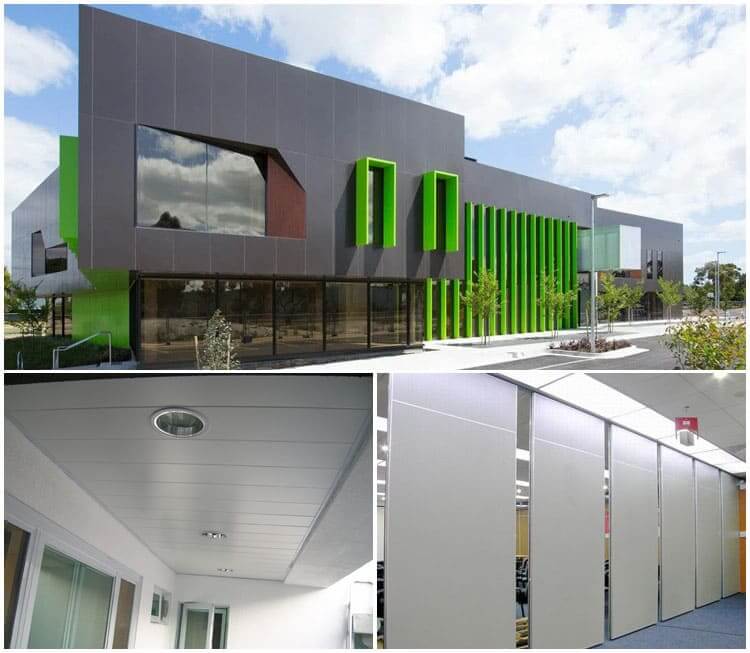

Aluminum alloy construction application
Electronic products: computers, mobile phones, refrigerator shells, radiators, etc.
Electronic product application
Kitchen supplies: aluminum pots, aluminum basins, rice cooker liners, household aluminum foil, etc.

Kitchen application
Packaging Of Aluminum Sheet/Coil
Every detail of packaging is where we pursue perfect service. Our packaging process as a whole is as follows:
Lamination: clear film, blue film, micro-mucosal, high-mucosal, laser cutting film (2 brands, Novacell and Polyphem);
Protection: paper corner protectors, anti-pressure pads;
drying: desiccant;
Tray: fumigated harmless wooden tray, reusable iron tray;
Packing: Tic-tac-toe steel belt, or PVC packing belt;
Material Quality: Completely free from defects such as white rust, oil spots, rolling marks, edge damage, bends, dents, holes, break lines, scratches, etc., no coil set.
Port: Qingdao or other ports in China.
Lead time: 15-45 days.
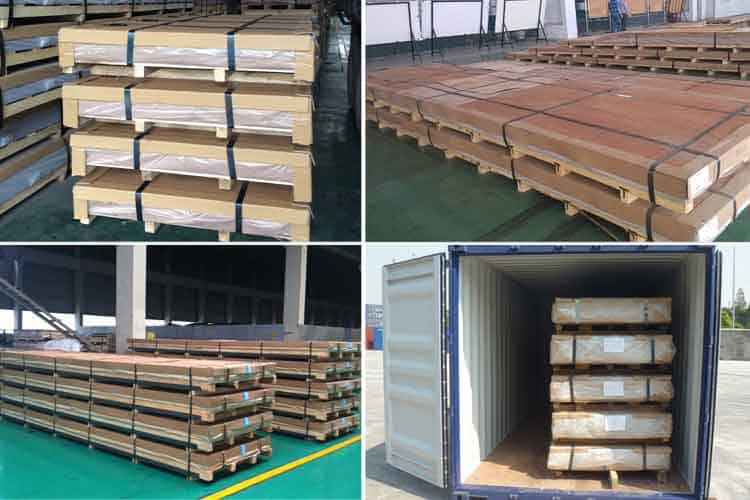

Aluminum sheet/plate packaging process
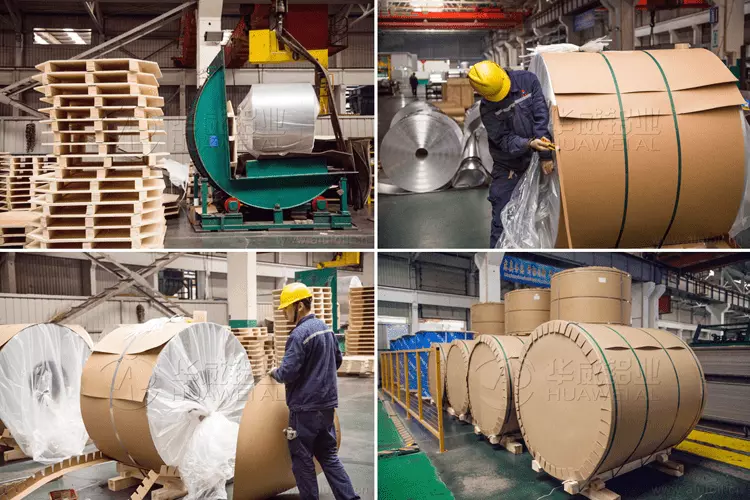

Aluminum coil packaging process
F: Are you a manufacturer or a trader?
Q: We are a manufacturer, our factory is at No.3 Weier Road, Industrial Zone, Gongyi, Henan, China.
F: What is the MOQ for ordering the product?
Q: Our MOQ is 5 tons, and some special products will have a minimum order quantity of 1 or 2 tons.
F: How long is your lead time?
Q: Generally our lead time is about 30 days.
F: Do your products have quality assurance?
Q: Yes, if there is a quality problem with our products, we will compensate the customer until they are satisfied.
Related Products
Latest Blogs
Ultra-high reflectivity aluminum mirror sheet
Ultra-high reflectivity aluminum mirror sheet with 95–98% visible reflectance, low scatter (TIS <1%), and specification advice for BRDF, spectral curves and coatings.
Trusted 3003 Aluminium Checker Plate Sheet Suppliers Worldwide
Find reliable 3003 Aluminium Checker Plate Sheet Suppliers offering certified quality, competitive pricing, custom sizes, and fast global delivery for your projects.
6061 T6 vs 7075 Aluminum: Strength, Weight & Best Uses
Compare 6061 T6 vs 7075 aluminum easily. Discover differences in strength, weight, and applications to choose the best for your projects.
Industrialization and Application of Honeycomb Aluminum Foil
This blog explores the industrialization of honeycomb aluminum foil, focusing on the 3003 alloy production process. It covers hot rolling, continuous casting, and the continuous casting-rolling method, highlighting the benefits of process optimization in improving mechanical properties, reducing energy consumption, and lowering production costs.